Signs and Symptoms
Overweight and obesity are conditions that are typically diagnosed based on an individual's body mass index (BMI), which is calculated based on their height and weight. A BMI between 25 and 29.9 is classified as overweight, while a BMI of 30 or above is classified as obese (World Health Organization, 2020).
While BMI is a useful screening tool, it does not take into account the distribution of body fat, which is an important predictor of health outcomes. Excess fat around the abdomen, also known as central obesity or visceral adiposity, has been linked to an increased risk of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease (World Health Organization, 2020).
In addition to BMI and body fat distribution, there are several signs and symptoms that may be associated with overweight and obesity:
Increased body weight: As the name suggests, overweight and obesity are characterized by an excessive amount of body weight.
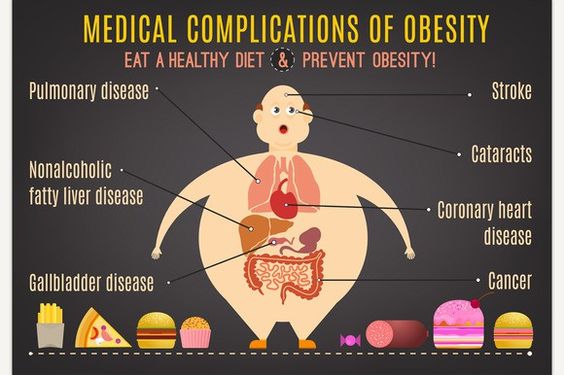
Difficulty breathing: Excess weight can put pressure on the lungs and make it more difficult to breathe, particularly during physical activity or when lying down.
Joint pain: The additional weight carried by the body can put strain on the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Fatigue: Carrying excess weight can make everyday activities more tiring and lead to feelings of fatigue and exhaustion.
Sleep apnea: Excess weight can lead to a condition called sleep apnea, which is characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep.
Skin problems: Overweight and obese individuals may experience skin problems such as skin irritation, rashes, or skin folds that are prone to infections.
Depression and anxiety: There is evidence to suggest that being overweight or obese can increase the risk of depression and anxiety, possibly due to social stigma and discrimination.
It's important to note that not all individuals who are overweight or obese will experience these signs and symptoms, and that the severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the individual's overall health status and other factors. Additionally, these symptoms may also be present in individuals who are not overweight or obese, highlighting the need for an individualized approach to diagnosis and management.
If you are experiencing any of these signs and symptoms or are concerned about your weight, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you determine your BMI, assess your overall health, and provide guidance on strategies to manage your weight and improve your health outcomes.
Reference:
World Health Organization. (2020). Obesity and overweight. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Comments
Post a Comment